TEMPORARY CONTRACEPTIVE METHOD
Introduction
Rapid population growth (96% in developing
countries) is a critical issue worldwide. Family
planning matters save women’s lives preventing
unintended pregnancies. Slower population growth
conserves resources, improves health and living
standards
Benefits of fertility control are interrelated.
Benefits are: Improved quality of life, better health,
less physical and emotional stress of life, better
education, job and economic opportunities. Benefits
are enjoyed by the couple, the children, other family
members, the community and the country.
Contraception and fertility control are not
synonymous.
the term contraception
includes all measures, temporary or permanent,
designed to prevent pregnancy due to the coital act.
METHODS OF CONTRACEPTION
TEMPORARY
Temporary methods are commonly used to post-
pone or to space births. However, the methods are
also frequently being used by the couples even though
they have got strong desire for no more children.
Barrier Methods
These methods prevent sperm deposition in the vagina
or prevent sperm penetration through the cervical
canal. The objective is achieved by mechanical
devices or by chemical means which produce sperm
immobilization, or by combined means.
™ Mechanical
Male — Condom
Female — Condom,diaphragm, cervical cap
™ Chemical
(Vaginal contraceptives)
Creams — Delfen (nonoxynol-9, 12.5 %)
Jelly — Koromex, Volpar paste
Foam tablets—Aerosol foams, Chlorimin T or
Contab, Sponge (Today)
™ Combination
Combined use of mechanical and chemical
Condom (male):
Condoms are made of polyure-
thane or latex. Polyurethane condoms are thinner and
suitable to those who are sensitive to latex rubber.
It is the most widely practised method used by the
male. In India, one particular brand (latex) is widely
marketed as ‘Nirodh’. The efficacy of condoms can be
augmented by improving the quality of the products
and by adding spermicidal agents during its use.
Protection against sexually transmitted disease is
an additional advantage. Occasionally, the partner
may be allergic to latex.
The method is suitable for couples who want to
space their families and who have contraindications
to the use of oral contraceptive or IUD. These are
also suitable to those who have infrequent sexual
intercourse.
Advantages
1. Cheaper with no contraindications
2. No side effects
3. Easy to carry, simple to use and disposable
4. Protection against sexually transmitted diseases, e.g.
gonorrhea, chlamydia, HPV and HIV
5. Protection against pelvic inflammatory diseases Disadvantages
6. Reduces the incidence of tubal infertility and ectopic
pregnancy
1. May accidentally break or slip off during coitus
2. Inadequate sexual pleasure
3. Allergic reaction (Latex)
4. To discard after one coital act
5. Failure rate — 15 (HWY)
7. Protection against cervical cell abnormalities
8. Useful where the coital act is infrequent
and irregular
Disadvantage
1. May accidentally break or slip off during coitus
2. Inadequate sexual pleasure
3. Allergic reaction (Latex)
4. To discard after one coital act
5. Failure rate — 15 (HWY)
Female condom (Femidom) :
It is a
pouch made of polyurethane which lines the vagina
and also the external genitalia. It is 17 cm in length
with one flexible polyurethane ring at each end.
Inner ring at the closed end is smaller compared to
the outer ring. Inner ring is inserted at the apex of the
vagina and the outer ring remains outside. It gives
Female condom
protection against sexually transmitted disease and
pelvic inflammatory disease. It is expensive. Multiple
uses can be made with washing, drying and with
lubrication. Failure rate is about 5–21/HWY.
Use of condom:
(1) As an elective contraceptive
method
(2) As an interim form of contraception during
pill use, following vasectomy operation (see later) and
if an IUD is thought lost until a new IUD can be fitted;
(3) During the treatment of trichomonal vaginitis of
the wife, the husband should use it during the courseof treatment irrespective of contraceptive practice;
(4) Immunological infertility — male partner to use
for 3 months. For other non-contraceptive benefits
Diaphragm
It is an intravaginal device made of latex with flexible
metal or spring ring at the margin. Its diameter varies
from 5–10 cm. It requires a medical or paramedical
personnel to measure the size of the device. The
distance between the tip of the middle finger placed
in the posterior fornix and the point over the fingerbelow the symphysis pubis gives the approximate
diameter of the diaphragm.
The device is introduced up to 3
hours before intercourse and is to be kept for at
least 6 hours after the last coital act. Ill fitting and
accidental displacement during intercourse increase
the failure rate.
Advantages
1. Cheap
2. Can be used repeatedly for a long time
3. Reduces PID/STIs to some extent
4. Protects against cervical precancer and cancer
Disadvantage
1. Requires help of a doctor or paramedical person to measure
the size required
2. Risk of vaginal irritation, abration and urinary tract infection
are there
3. Not suitable for women with uterine prolapse
Vaginal Contraceptives
Spermicides: Spermicides are available as vaginal
Spermicides gel
foams, gels, creams, tablets and suppositories.
Usually, they contain surfactants like nonoxynol–9,
octoxynol or benzalkonium chloride. These agents
mostly cause sperm immobilization. The cream or
jelly is introduced high in the vagina with the help
of the applicator soon before coitus. Foam tablets
(1–2) are to be introduced high in the vagina at least
5 minutes prior to intercourse. In isolation, it is not
effective (18–29 HWY), but enhances the efficacy of
condom or diaphragm when used along with it. There
may be occasional local allergic manifestations either
in the vagina or vulva.
Vaginal contraceptive sponge (Today): It is made of
polyurethane impregnated with 1 g of nonoxynol-9
as a spermicide. Nonoxynol-9 acts as a surfactant
which either immobilizes or kills sperm. It releases
spermicide during coitus, absorbs ejaculate and
blocks the entrance to the cervical canal. The
sponge should not be removed for 6 hours after
intercourse. Its failure rate (HWY) is about —
Parous women: 32-20, Nulliparous 16-9.
Fertility Awareness Method
Fertility
Awareness Method requires partner’s cooperation.
The woman should know the fertile time of her
menstrual cycle.
Advantages
• No cost
• Lack of side effects
Disadvantages
• Difficult to calculate the safe period reliably
• Needs several months training to use these methods
• Compulsory abstinence from sexual act during certain periods
• Not applicable during lactational amenorrhea or when the periods
are irregular
Rhythm Method:
This is the only method approved by
the Roman Catholic Church. The method is based on
identification of the fertile period of a cycle and to
abstain from sexual intercourse during that period.
This requires partner’s cooperation
(a) recording of previous
menstrual cycles (calendar rhythm)
(b) noting the
basal body temperature chart (temperature rhythm)
and
(c) noting excessive mucoid vaginal discharge
Coitus Interruptus (withdrawal) :
It is the oldest and probably the most widely accepted
contraceptive method used by man. It necessitates
withdrawal of penis shortly before ejaculation.
It requires sufficient self-control by the man so that
withdrawal of penis precedes ejaculation.
Breastfeeding, Lactational amenorrhea (LAM):
Prolonged and sustained breastfeeding offers a natural
protection of pregnancy
This is more effective in
women who are amenorrheic than those who are
menstruating. The risk of pregnancy to a woman who
is fully breastfeeding and amenorrheic is less than 2
percent in the first 6 months. Otherwise, the failure
rate is high (1–10%).
Fertility awareness based methods are:
(1) Natural
contraception (Rhythm method, Coitus interruptus
and Lactational amenorrhea method) (2) Barrier
method (Condoms, diaphragm and spermicides).
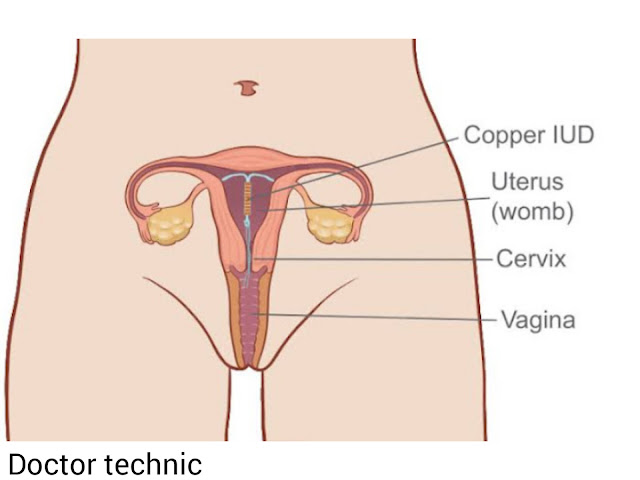
Intrauterine contraceptive
devices (IUCDs)
The intrauterine device have been used throughout the
world. During the last couple of decades, however,
there has been a significant improvement in its design
and content. The idea is to obtain maximum efficacy
without increasing the adverse effects.
Lippes loop, Cu T, Cu 7,
Multiload and Progestasert are examples of open
devices.
Hormone containing IUD
• Cu T 200 • Multiload 250 • Multiload 375
• Cu T 380A • LNG – IUS • GyneFix
IUD (Cu devices and hormone releasing IUDs)
Advantages
1. Inexpensive : Cu T-distributed free of cost through
Government channel
2. Simplicity in techniques of insertion and most cost
effective of all methods
3. Prolonged contraceptive protection after insertion
(5–10 years) and suitable for the rural population of
developing countr
4. Systemic side effects are nil. Suitable for hypertensives,
breastfeeding women and epileptics
5. Reversibility to fertility is prompt after removal
Disadvantage
1. Require motivation
2. Limitation in its use
3. Adverse local reactions manifested by menstrual
abnormalities, PID, pelvic pain and heavy periods.
Beside effects are less with third generation of IUDs
4. Risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Contraceptive devices (Copper - t )








.png)



.png)






0 Comments