Introduction:
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers that affect women worldwide. According to the American Cancer Society, breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death among women. In this blog, we will discuss breast cancer in detail, including the causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
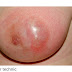
General breats image
What is Breast Cancer?
Breast cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the breast tissue. It occurs when the cells in the breast tissue start growing abnormally and uncontrollably, forming a mass or a lump. These abnormal cells can spread to other parts of the body through the lymphatic system or the bloodstream, leading to metastatic breast cancer.
Types of breast cancer
Causes of Breast Cancer:
The exact cause of breast cancer is unknown, but there are some factors that can increase the risk of developing breast cancer, including:
Gender: Breast cancer is more common in women than in men.
Age: The risk of developing breast cancer increases with age.
Family history: Women with a family history of breast cancer, especially those with a first-degree relative (mother, sister, or daughter) who had breast cancer, have a higher risk of developing the disease.
Genetic mutations: Certain gene mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, can increase the risk of developing breast cancer.
Hormonal factors: Hormonal factors, such as early onset of menstruation, late onset of menopause, and having children at an older age, can increase the risk of breast cancer.
Lifestyle factors: Lifestyle factors, such as alcohol consumption, obesity, and physical inactivity, can increase the risk of breast cancer.
Signs and Symptoms of breast cancer
Symptoms of Breast Cancer:
The symptoms of breast cancer can vary from person to person. Some women may not have any symptoms, while others may experience one or more of the following:
A lump or thickening in the breast or underarm area.
Nipple discharge, other than breast milk.
Changes in the size or shape of the breast.
Changes in the texture of the breast skin, such as dimpling or puckering.
Redness or rash on the breast skin.
Swelling or lump in the lymph nodes under the arm.
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, such as cysts or benign tumors. If you notice any changes in your breast, it is important to consult your doctor for an evaluation.
Diagnosis of breast cancer
Diagnosis of Breast Cancer:
Breast cancer can be diagnosed through various methods, including:
Mammography: A mammogram is an X-ray of the breast tissue that can detect breast cancer at an early stage, even before a lump can be felt.
Breast ultrasound: An ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the breast tissue, which can help detect lumps or other abnormalities.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): An MRI uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the breast tissue, which can help detect breast cancer.
Biopsy: A biopsy involves taking a small tissue sample from the breast and examining it under a microscope to determine if it is cancerous.
Treatment of breast cancer:
depends on several factors, including the stage of the cancer, the size and location of the tumor, and the woman's overall health. The goal of treatment is to remove the cancer and prevent it from spreading or coming back. The treatment options for breast cancer include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and hormone therapy.
Surgery:
Surgery is the most common treatment for breast cancer. The type of surgery depends on the stage and size of the cancer. There are two main types of surgery for breast cancer:
Lumpectomy: A lumpectomy involves removing the cancerous tissue and a small amount of surrounding healthy tissue.
Surgergically remove of breast cancer
Mastectomy: A mastectomy involves removing the entire breast.
In some cases, a woman may choose to have breast reconstruction surgery after a mastectomy. This involves rebuilding the breast using a breast implant or tissue from another part of the body.
Radiation Therapy:
Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. It is often used after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells. Radiation therapy can also be used before surgery to shrink the tumor and make it easier to remove.
Radiation therapy is usually given five days a week for several weeks. The treatment itself is painless, but it can cause side effects such as fatigue, skin irritation, and breast swelling.
Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells and prevent them from spreading. It is often used after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells. Chemotherapy can also be used before surgery to shrink the tumor and make it easier to remove.
Chemotherapy is usually given intravenously, but it can also be taken orally. The treatment is usually given in cycles, with rest periods in between. Chemotherapy can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, hair loss, and fatigue.
Hormone Therapy:
Hormone therapy is used to treat breast cancers that are hormone receptor-positive. These cancers have receptors for estrogen or progesterone, which means that hormones can fuel their growth. Hormone therapy works by blocking the effects of these hormones or by lowering their levels in the body.
Hormone therapy can be given in several ways, including:
Tamoxifen: Tamoxifen is a pill that is taken daily for five to ten years.
Aromatase inhibitors: Aromatase inhibitors are pills that are taken daily for five to ten years. They work by blocking the production of estrogen.
Ovarian suppression: Ovarian suppression involves stopping the ovaries from producing estrogen. This can be done with surgery or with medications.
Side effects of hormone therapy can include hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and mood changes.
Targeted Therapy:
Targeted therapy is a newer type of treatment that is used for some types of breast cancer. It works by targeting specific proteins on the surface of cancer cells, which can stop or slow their growth. Targeted therapy can be given as a pill or as an intravenous infusion.
Some of the targeted therapy drugs used to treat breast cancer include:
Herceptin (trastuzumab): Herceptin is used to treat breast cancers that are HER2-positive. These cancers have too much of a protein called HER2, which makes them grow faster. Herceptin works by blocking HER2 and slowing the growth of cancer cells.
Perjeta (pertuzumab): Perjeta is another drug that is used to treat HER2-positive breast cancers. It works by blocking a different part of the HER2 protein than Herceptin.
Side effects of targeted therapy can include fatigue, nausea, and diarrhea.
Conclusion:
Breast cancer is a serious disease, but there are many treatment options available. The choice of treatment depends on several factors.
~ Thank you for reading .....






.png)


.png)






0 Comments